
A stamping die is a special process equipment for processing materials (metallicor non-metallic) into parts (or semi-finishedducts) in a cold stamping process called a cold stamping die (commonly known as a cold punch die). stamping is a pretemperature using a die mounted on apress to produce separation or plastic deformation.
At Kuasu Moldtec, we specialize in providing high-quality Sheet Metal Stamping Dies for a wide range of industries, including automotive, consumer electronics, home appliances, medical devices, and more. With over a decade of experience, we have established ourselves as a trusted partner in precision metal stamping, offering state-of-the-art tooling and unmatched technical expertise to deliver the best solutions for your manufacturing needs.
Sheet metal stamping is a cold-forming process that uses a die to shape flat metal sheets into specific parts or components. This process is widely used to produce high-precision metal parts in large volumes, with applications ranging from automotive body panels to consumer electronics enclosures.
The process begins with a flat metal sheet, typically made from materials such as steel, aluminum, copper, or brass, which is fed into a stamping press. The die is used to cut, bend, or emboss the sheet metal, creating the desired shape. The precision and efficiency of this method make it an excellent choice for producing high-quality, complex parts at scale.
At Kuasu Moldtec, we offer a variety of sheet metal stamping dies tailored to the specific needs of our customers. These include:
Progressive Dies: These dies are used for high-volume, multi-step operations. As the metal sheet moves through the die, it undergoes multiple stages of stamping, such as cutting, bending, and forming, with each pass producing a more complex part. Progressive dies are ideal for producing large quantities of small to medium-sized parts with high precision.
Single-Action Dies: These dies perform a single operation, such as cutting, punching, or bending. Single-action dies are typically used for smaller production runs or for creating parts that do not require multiple operations.
Compound Dies: Compound dies are capable of performing two or more operations simultaneously on a single stroke, such as cutting and bending. This makes them an excellent choice for parts that require multiple processes in a single press cycle.
Blanking Dies: These dies are used to cut out flat, shaped metal parts from a larger sheet. Blanking is often the first step in the stamping process, producing the base shape that will undergo further operations, such as bending or embossing.
Forming Dies: Forming dies are used to shape sheet metal into a 3D part through processes like deep drawing, stretching, or bending. These dies are commonly used in applications where parts need to maintain specific geometric shapes, such as in the automotive industry.
We work with a variety of materials to suit the specific needs of your project. Some of the most commonly used materials in sheet metal stamping include:
Steel: Steel is the most commonly used material due to its durability, strength, and cost-effectiveness. It is suitable for a wide range of applications, from automotive parts to industrial components.
Aluminum: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has excellent formability, making it an ideal material for industries that require high-performance, lightweight parts, such as the automotive and consumer electronics sectors.
Copper: Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications in electronics and electrical components.
Brass: Brass offers good corrosion resistance and is highly formable, making it suitable for decorative applications and electrical components.
Stainless Steel: Stainless steel is resistant to rust and corrosion and is often used in medical devices, kitchen appliances, and automotive parts that require superior durability.
There are several key advantages to using sheet metal stamping dies in the manufacturing process:
High Precision: Stamping dies provide high accuracy and consistency, making them ideal for producing parts that require tight tolerances and intricate details.
Cost-Effective for High-Volume Production: Once the die is created, it can be used to produce large quantities of identical parts quickly and at a low cost per unit.
Versatility: Sheet metal stamping can accommodate a wide range of materials, thicknesses, and part geometries, making it suitable for diverse applications across various industries.
Speed and Efficiency: The automated nature of the stamping process allows for fast production speeds, reducing lead times and enabling the rapid delivery of high-volume orders.
Minimal Waste: The stamping process is highly efficient, with minimal material waste, making it an environmentally friendly option compared to other manufacturing methods.
At Kuasu Moldtec, we offer comprehensive sheet metal stamping die services to meet the unique needs of our customers:
Custom Die Design: Our experienced engineers collaborate closely with you to design custom stamping dies that meet your exact specifications. Whether you need simple or complex parts, we have the expertise to deliver a solution that works for your application.
Prototyping: We provide prototype stamping services to help you validate your design before committing to full-scale production. This allows you to test the functionality, fit, and performance of your part before moving forward.
High-Volume Production: Our advanced stamping presses and automated systems enable us to efficiently produce large volumes of parts with consistent quality and minimal lead time.
Tooling and Die Maintenance: We offer ongoing tooling maintenance and repair services to ensure that your stamping dies continue to perform at their best over time. Proper maintenance helps extend the life of the die and reduces downtime.
Post-Stamping Services: We also offer secondary operations such as deburring, machining, painting, coating, and assembly, ensuring that your parts are ready for immediate use or integration into larger assemblies.
Read More
Stamping Die

Progressive die
2out LH/RH Material: STEEL, GRADE 6 TYPE 340XF MPAPS A-6 Gauge:5.0t Tonnage: 1600t

Blank size:5.0T*877W*240P

Part name:HINGE,HOOD GOR L/R

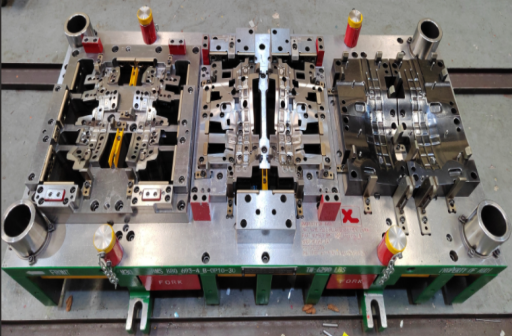
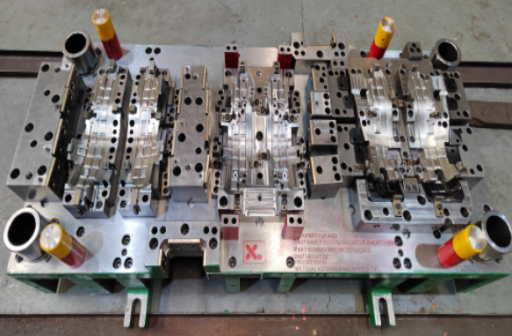
Auto Transfer Die
2out LH/RH Material: GMW2M-ST-S-CR2-HD60G60G-U Gauge:0.7t Tonnage: 1200t
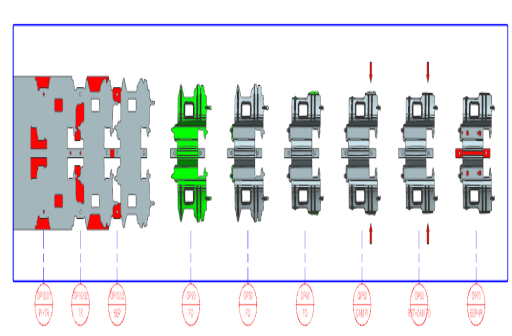
Blank size
0.7T*746W*420P

Part name:REINFORCEMENT -F/FDR
OP20.FO OP30.TR OP40.TR
OP50.FO OP60.FO+RST OP70.PI

OP05 Blanking die 2 out
Process: prog die+ hand transfer die Material: A653M-EDDS Z90 Gauge:0.8t Tonnage: 200T+300T+300T
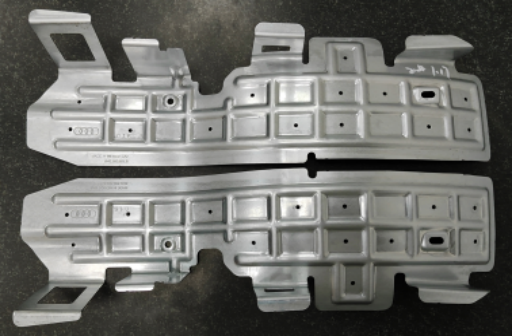
Part name:PSD C-PILLAR DEFO ELEMENT

Draw parts

Security framework parts

Air bag parts

Electronic parts

Aluminum parts

High strength parts from ES780 to ES1180